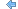Use For intervals greater than 1 year, show to designate whether to use annualized or cumulative return calculations in the Performance Data Extract bulk report. Intervals less than one year will always use cumulative returns.
You can choose:
-
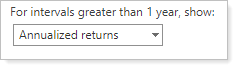
Annualized returns. In this example, the date range is five years. The report calculates an annualized return for each account's Gross TWR and Net TWR.
-
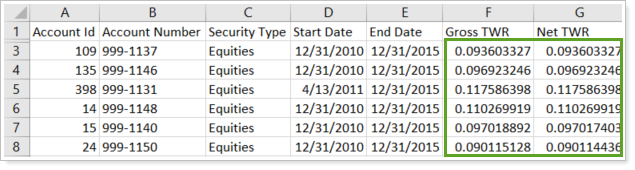
Cumulative returns. In this example, the date range is five years. The report calculates a cumulative return for each account's Gross TWR and Net TWR.
What Is Annualization?
Annualization converts a cumulative rate over a number of years to the average yearly rate that, when compounded over the entire period, results in the cumulative rate. The goal of annualization is to normalize returns and state them in terms of what has been achieved in an average year for the account or position. This makes it easier to compare the performance an account has achieved relative to others that have been open for different lengths of time.
You might want to use this when using the report for comparisons: comparing accounts to a benchmark, comparing account data for different advisors, or comparing positions that have been held for differing periods of time.
We recommend that you annualize returns if you're doing a comparison and your time period is a year or longer. This ensures that you're comparing apples to apples.
Learn More
For more information about the Performance Data Extract bulk report, see Performance Data Extract Bulk Report.
For more information on bulk reports, see Understanding Bulk Data Exports.